What is Otology?
Otology is the branch of medicine that deals with the study of the Ear and its diseases. This discipline is part of Otorhinolaryngology , a specialty dedicated to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT).
What diseases does Otology Treat?
Otology focuses on treating ear problems and, therefore, hearing and balance Problems. The ear has a fundamental role in balance and the feeling of vertigo or dizziness. Thus, some of the most frequent Pathologies in the Otology consultation are the following:
- Otitis or ear infections: they are very common, especially in babies and children.
- Tinnitus or tinnitus : annoying perception of sound or constant beeping, which does not even allow you to hear clearly.
- Barotrauma : a barotrauma in the ear is an injury produced by changes in barometric pressure (air) or water.
- Menière’s disease : it is a common cause of vertigo and dizziness, due to fluid problems in the middle Ear. It also tends to cause tinnitus.
What subspecialties are there within Otology?
Otology focuses on the study of the Ear, being a subspecialty within Otolaryngology. Even so, each professional can specialize in a specific pathology or in a part of the ear (outer, middle and Inner Ear), such as Damage to the Eardrum or Middle Ear Surgery .
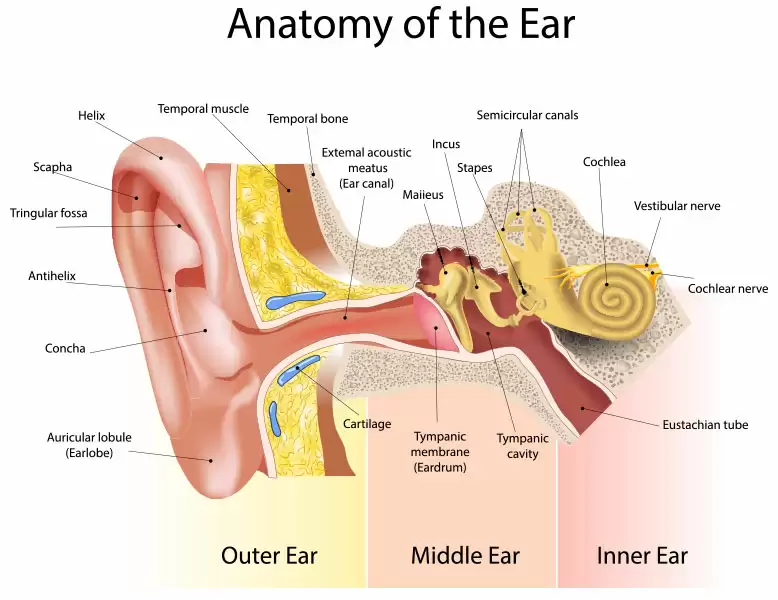
Ear side of the head, it is divided into outer, middle and inner ear of three parts. The auricle of the outer ear is the part called “Ear” that is exposed on the surface. It is composed of elastic cartilage as a scaffold and overlying skin, and there is very little connective tissue under the skin.
Extending from the auricle into the skull is the external auditory canal. It is a curved channel, sometimes with brownish-yellow oily secretions that cover the tympanic membrane.
The tympanic membrane is an oval translucent membrane between the outer ear and the middle Ear. There are mainly three ossicles in the middle ear, called malleus, incus and stapes. The three small bones are connected between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear.
Another important part of the middle Ear is the Eustachian tube, which opens downward into the nasopharynx.
The inner Ear is located in the hard bone of the temporal bone, the main part is the semicircular canal and the cochlea. Semicircular canal is a set of complicated lumens. It is composed of three mutually perpendicular semicircular canals, front, back and outer. The cochlea is a curly bone tube shaped like a snail shell, connected to the auditory nerve.
Outer ear to Collect Sound Waves
Outer ear function is through the special shape of the pinna and external auditory canal, collecting sound waves coming from the outside world. When sound waves reach the tympanic membrane, they cause it to vibrate.
The middle Ear Sound Transmission shock
Eardrum vibrations will drive the three ossicles in the middle ear. They in turn transmit the vibration of sound waves into the cochlea of the inner ear. The Eustachian tube in the middle ear plays a role in regulating the air pressure and hearing in the middle ear.
Inner Ear Signal Transmission
There are special receptors in the cochlea of the inner ear, which convert sound waves into biological signals, and then transmit them to the auditory nerve, which enters the auditory function area of the brain.
Controlling the Balance of the body
The function of the semicircular canal is to sense the changes in the body’s posture, and to convey the information of this change to the brain center to coordinate the control of the body’s balance.
Often the Ear Common Disease:
- Acute otitis media
- Deafness
- Tinnitus
- Puncture of tympanic membrane
Ear Common Symptoms:
- Earache
- Tinnitus
- Ear rash
- Deaf
First aid of Ear Injuries: Foreign body in the ear
Ear Care
- Do not dig the ears, especially not with a small object to titillate, to avoid too much noise place.
- If you accidentally get water into your ears, try to pat it dry gently.
- Do not abuse ear drops.